- Home
- Solutions
- Foot care & Diabetic Solution
- Gangrene treatment
- emergency & intensive care
emergency & intensive care
emergency & intensive care
Table of Content
2. Types of Intensive Care Units (ICUs)
3. Cardiac Intensive Care Unit (CICU)
4. Surgical Intensive Care Unit (SICU)
5. Neonatal Intensive Care Unit (NICU)
6. Pediatric Intensive Care Unit (PICU)
7. Concept and Functions of ICU
8. Purpose and Importance of Intensive Care
9. Conclusion
10. Faqs
Introduction
When we talk about emergency and intensive care, we’re diving into the very heart of modern medicine. It’s the place where critical moments decide between life and death — a field built on precision, compassion, and relentless innovation. But what does intensive care actually mean? And why is it such a vital component of every hospital?
The meaning of intensive care revolves around providing continuous, specialized monitoring and advanced treatment for patients who are critically ill or unstable. These patients may have life-threatening conditions, such as severe infections, trauma, organ failure, or complications after surgery. Unlike a general hospital ward, an intensive care unit (ICU) is equipped with advanced medical technology, a higher nurse-to-patient ratio, and round-the-clock medical attention.
So, what is an intensive care unit exactly? Simply put, it’s a specially designed hospital section dedicated to managing patients who need intensive medical supervision and treatment. Every aspect of an ICU—from its equipment to its staff training—is tailored to stabilize patients, prevent complications, and support recovery.
The purpose of an intensive care unit is not just to treat emergencies, but to offer a bridge between life-threatening conditions and recovery. Whether it’s a heart attack patient in a Cardiac Intensive Care Unit (CICU) or a newborn in a Neonatal Intensive Care Unit (NICU), ICUs provide the highest standard of care in the most critical moments.
There are several types of intensive care units, each specialized to cater to different medical needs. These include the Cardiac ICU, Surgical ICU, Neonatal ICU, and Pediatric ICU, among others. Each has its own protocols, equipment, and staff training tailored to the patients it serves.
In short, intensive care is not just a place—it’s a philosophy of medicine. It’s where science, technology, and humanity meet to fight for every heartbeat.
Types of Intensive Care Units (ICUs)
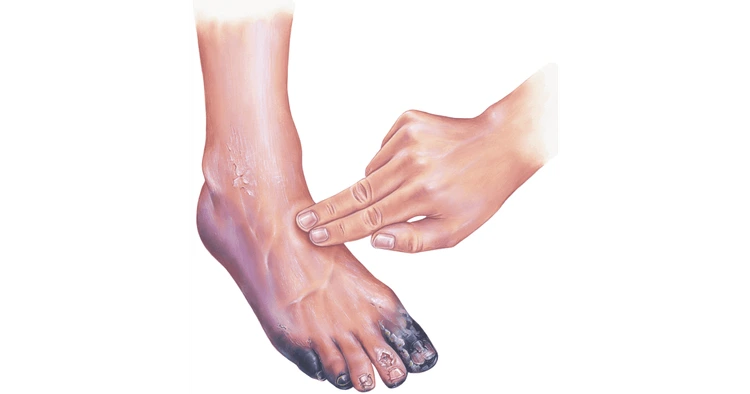
Every patient in critical condition has unique medical needs, and that’s why hospitals have developed specialized intensive care units (ICUs). These units ensure that each patient receives care designed precisely for their health issue. Let’s dive into the major types of intensive care units and what makes each one vital to modern healthcare.In some cases we also provide gangrene treatment without surgery, helping avoid invasive procedures
Prevention is key — but if ulceration progresses despite measures, our Emergency & Intensive Care facility
is ready to intervene, ensuring immediate support for patients facing life-threatening infections like gangrene or diabetic complications.
Cardiac Intensive Care Unit (CICU)
- The Cardiac Intensive Care Unit, also known as the Coronary Care Unit (CCU), is dedicated to patients suffering from severe heart conditions. These can include heart attacks, cardiac arrhythmias, heart failure, or those recovering from heart surgery. The focus of the CICU is on immediate stabilization, continuous monitoring, and advanced interventions to restore normal heart function.
- Inside a CICU, patients are surrounded by cutting-edge medical technology — cardiac monitors, ventilators, and defibrillators — all managed by a team of highly trained cardiologists, cardiac nurses, and respiratory therapists. Every second counts here, and constant vigilance ensures that any change in a patient’s condition is detected and treated immediately.
- Patient care procedures in the CICU include regular electrocardiograms (ECGs), blood pressure monitoring, oxygen therapy, and sometimes mechanical ventilation. The staff also ensures emotional support, as cardiac emergencies can be both physically and mentally stressful.
- Protocols in cardiac intensive care focus on infection control, medication management, and post-surgical monitoring. Doctors use evidence-based strategies to prevent complications, improve survival rates, and prepare patients for rehabilitation. The CICU, therefore, stands as a symbol of how medical science and compassion come together to save lives — one heartbeat at a time.
Surgical Intensive Care Unit (SICU)
The Surgical Intensive Care Unit (SICU) caters to patients recovering from major surgeries or suffering from severe trauma that requires surgical intervention. It’s a hub of precision, where surgeons, anesthesiologists, and critical care specialists work hand-in-hand to ensure smooth recovery after complex operations.
Patients admitted to the SICU might have undergone procedures such as organ transplants, major abdominal or orthopedic surgeries, or neurosurgical operations. The main purpose of the SICU is to closely monitor vital signs, manage pain, and prevent post-surgical complications such as infections, internal bleeding, or respiratory issues.
What makes the SICU unique is its specialized equipment — advanced ventilators, hemodynamic monitors, and infusion pumps — all designed to support vital organs during recovery. The nursing staff is specially trained to detect early warning signs of complications and act swiftly.
Infection control is also a major priority here. Because post-operative patients have a higher risk of infection due to surgical wounds and weakened immunity, sterile protocols and hygiene measures are strictly enforced. From hand hygiene to sterilizing instruments, every detail matters.
Ultimately, the SICU ensures that patients get the intensive post-operative care they need to recover safely and return to normal life. It’s a place of healing, vigilance, and teamwork.
Neonatal Intensive Care Unit (NICU)
The Neonatal Intensive Care Unit (NICU) is one of the most sensitive and emotionally charged areas of any hospital. It’s where premature or critically ill newborns receive specialized care and round-the-clock monitoring. These tiny patients might be born before 37 weeks of gestation, have low birth weight, or face complications such as respiratory distress, infections, or congenital conditions.
NICUs are equipped with state-of-the-art incubators, ventilators, and feeding systems that mimic the safety and warmth of the womb. The primary goal is to stabilize and nurture newborns until they are strong enough to survive without medical support. The staff — including neonatologists, neonatal nurses, and respiratory therapists — are experts in caring for fragile newborns who need specialized attention.
A major concern in the NICU is infection control. Because newborns have immature immune systems, even a minor infection can become life-threatening. Hospitals follow strict protocols, including sterilized equipment, limited visitor access, and frequent disinfection. Hand hygiene, the use of personal protective equipment (PPE), and controlled air filtration systems are standard practices to ensure the safest environment possible.
An excellent example of such specialized care is the Neocare Neonatal Intensive Care Unit, which emphasizes infection prevention, advanced monitoring, and compassionate parental involvement. Facilities like Neocare show how innovation and empathy can coexist in modern neonatal medicine.
For many parents, the NICU is an emotional rollercoaster — filled with anxiety, hope, and courage. But thanks to continuous advancements and dedicated professionals, survival rates and outcomes for premature babies have improved tremendously over the years.
Pediatric Intensive Care Unit (PICU)
The Pediatric Intensive Care Unit (PICU) is designed for children beyond the newborn stage who are facing life-threatening conditions. These can include severe infections, accidents, organ failure, or post-surgical recovery needs. In this specialized unit, care is not only medical but also deeply psychological — addressing both the physical and emotional well-being of young patients.
Doctors in the PICU specialize in pediatric critical care medicine, ensuring that every intervention considers the unique physiology and needs of children. The staff uses child-friendly approaches to reduce fear and anxiety, making sure that the environment supports healing in every sense.
Like other ICUs, the PICU also emphasizes infection control, pain management, and precise monitoring. The equipment is adapted for children’s sizes and sensitivities, ensuring safe and effective treatment.
Ultimately, the PICU represents the heart of pediatric medicine — a place where expertise, technology, and compassion unite to give children a fighting chance at recovery.
Concept and Functions of ICU
- The concept of the Intensive Care Unit (ICU) revolves around one central idea — providing the most advanced, continuous, and life-saving care possible for critically ill patients. Every ICU is a microcosm of modern medical innovation, blending technology, expertise, and compassion to sustain life when the body itself struggles to do so.
- At its core, an ICU is more than just a hospital department; it’s a critical care ecosystem. It functions through collaboration between specialized doctors, nurses, respiratory therapists, and other healthcare professionals. These experts are trained to respond instantly to changes in a patient’s condition, ensuring immediate intervention when seconds can mean the difference between life and death.
- ICUs are equipped with sophisticated monitoring systems, ventilators, infusion pumps, dialysis machines, and other life-support equipment. Each device plays a crucial role in maintaining vital organ function — whether it’s supporting breathing, stabilizing blood circulation, or regulating heart rhythm. In addition, constant observation of vital parameters such as heart rate, oxygen levels, and blood pressure allows the team to make swift medical decisions.
- Another major function of the ICU is infection control. Because ICU patients often have compromised immune systems, they are more vulnerable to infections. Hospitals apply rigorous infection prevention protocols — including sterilization of medical instruments, isolation rooms, air filtration systems, and strict hygiene procedures. Healthcare workers adhere to “universal precautions,” ensuring hand hygiene and protective gear use at all times. The goal is simple but vital: protect the patient from hospital-acquired infections that could complicate their condition.
- In addition to technical care, one often-overlooked aspect of ICU management is sleep in the intensive care unit. Patients in critical care environments frequently experience disrupted sleep due to constant monitoring, noise, and lighting. Yet, adequate rest is essential for recovery — it supports immune function, stabilizes hormones, and promotes mental health. Hospitals are increasingly introducing sleep-promoting measures such as noise reduction, dimmed lighting at night, and scheduled rest periods to help patients recover faster.
- In summary, the ICU concept is about balance — balancing technology and human touch, urgency and precision, intervention and recovery. It’s where medicine reaches its highest form of teamwork and innovation, proving that every heartbeat matters.
Purpose and Importance of Intensive Care
- The purpose of the Intensive Care Unit (ICU) is clear and profound: to save lives by providing immediate, specialized, and comprehensive care to critically ill patients. Whether it’s a victim of a car accident, someone suffering a stroke, or a newborn fighting to breathe, the ICU is the safety net that prevents tragedy through timely intervention.
- The ICU serves as the first line of defense during medical emergencies. Its role begins the moment a patient’s condition becomes unstable — for instance, when vital organs begin to fail, or when the risk of sudden deterioration is high. The ICU team takes charge with precision, using advanced tools to stabilize the patient, diagnose the cause, and initiate targeted treatments. Continuous monitoring ensures that every fluctuation in heart rate, oxygen saturation, or blood pressure is detected and addressed immediately.
- Beyond emergency response, the ICU is also central to ongoing life support and recovery. Some patients require ventilators to assist with breathing, dialysis to support kidney function, or intravenous medications to maintain heart rhythm and blood pressure. Each of these interventions is carefully calibrated and constantly supervised. The ICU’s multidisciplinary team collaborates closely, holding daily rounds to reassess treatment plans and optimize outcomes.
- Another significant purpose of the ICU is to act as a bridge to recovery. Once patients are stabilized, the focus gradually shifts from crisis management to rehabilitation and long-term recovery planning. This includes physical therapy, nutritional support, and mental health counseling — all of which help patients transition safely out of the ICU.
- To learn more about advanced critical care and patient recovery solutions, visit Mobility Solution, where expert care meets modern medical innovation.
- The importance of the ICU extends beyond individual patients. It plays a vital role in the overall hospital ecosystem. Without it, hospitals would lack the capacity to manage emergencies effectively or perform complex surgeries safely. Intensive care also contributes to medical research, training, and innovation — constantly improving standards of care through new technologies and evidence-based practices.
- In essence, the ICU embodies the mission of modern medicine: to preserve life, alleviate suffering, and restore health. It’s a place where science meets empathy, and where every effort is made to turn the impossible into the possible.
Conclusion
The world of Emergency and Intensive Care is one of extraordinary precision, urgency, and compassion. It represents the pinnacle of modern healthcare — a field where every heartbeat, every breath, and every second counts. The Intensive Care Unit (ICU) is not just a department within a hospital; it is a sanctuary of survival, where medicine, technology, and humanity converge to save lives when all else seems uncertain.
Through the different types of intensive care units — including the Cardiac ICU (CICU), Surgical ICU (SICU), Neonatal ICU (NICU), and Pediatric ICU (PICU) — hospitals are able to deliver specialized care tailored to the needs of every critically ill patient. Whether it’s a newborn struggling for their first breath or an elderly patient recovering from major surgery, these units provide the expertise, vigilance, and equipment required to sustain life and encourage recovery.
For a detailed overview of emergency services, critical care procedures, and specialized ICU support, you can explore Emergency & Intensive Care at Innayat Medical.
The concept of intensive care revolves around constant monitoring, advanced life support, and teamwork. Infection control remains a cornerstone of ICU operations, ensuring that patients, already vulnerable, are protected from further complications. Meanwhile, attention to aspects like sleep in the intensive care unit and emotional well-being demonstrates the holistic approach that defines today’s critical care environment.
The purpose of intensive care units extends beyond treating medical emergencies. It’s about giving patients a second chance — an opportunity to heal, to recover, and to return to life. These units are the backbone of any hospital, ensuring readiness for all types of crises, from cardiac arrest to trauma, surgical complications, or neonatal distress. Without intensive care, modern medicine would lack its most powerful tool in the fight to preserve life.
As we look to the future of emergency and intensive care, technological innovation continues to revolutionize the field. Artificial intelligence, predictive analytics, tele-ICU systems, and robotic assistance are enhancing decision-making, improving accuracy, and enabling remote care. Meanwhile, human compassion — the irreplaceable force behind every successful recovery — remains at the heart of every ICU team.
In conclusion, Emergency and Intensive Care is more than just medical intervention; it is a promise — a promise that no matter how critical the condition, every patient deserves the best possible chance at survival and recovery. It is where courage meets expertise, where science meets the soul, and where hope is kept alive against all odds.
Learn everything about Emergency & Intensive Care, including ICU types such as cardiac, surgical, and neonatal, their purpose, functions, infection control, and patient care protocols.
Enquiry Now