- Home
- Prosthetic Products
- Prosthetic Hands: Cost in India, Types, and How They Work
Prosthetic Hands: Cost in India, Types, and How They Work

Table of Content
2. What Are Prosthetic Hands?
3. Types Of Prosthetic Hands
4. How Do Prosthetic Hands Work?
5. Factors Affecting Prosthetic Hand Cost
6. Prosthetic Hand Cost In India
7. Choosing The Right Prosthetic Hand
8. Accessibility And Availability In India
9. Care, Maintenance, And Lifespan Of Prosthetic Hands
10. Success Stories: Real-Life Impact Of Prosthetic Hands
11. Conclusion
Introduction
Prosthetic hands are life-changing innovations that provide individuals with hand loss or limb difference a chance to regain independence, functionality, and confidence. These artificial devices are designed to mimic the natural hand in appearance and, in more advanced models, even in movement and grip. Whether a person has lost a hand due to an accident, a medical condition, or a congenital anomaly, prosthetic hands offer a powerful solution to enhance mobility and quality of life.
In this detailed guide, we will explore everything you need to know about prosthetic hands—from their types and how they work to the costs associated with them in India. Whether you're considering one for yourself or a loved one, understanding the options and affordability of prosthetic hand technology is key to making an informed decision.
What Are Prosthetic Hands?
Prosthetic hands are artificial devices designed to replicate the function and appearance of a human hand. They are part of the broader field of prosthetics, which involves the design, fabrication, and fitting of custom-made limbs and body parts for people who have lost them or were born without them.
People may require prosthetic hands due to various reasons, including:
- Traumatic injuries (accidents, war injuries, etc.)
- Medical conditions (like cancer or diabetes leading to amputation)
- Congenital limb differences (born without a hand or fingers)
The goal of a prosthetic hand is not just cosmetic. Modern prosthetic hands offer varying levels of functionality, allowing users to perform daily activities such as grasping objects, writing, or using a computer. Technological advancements have made these devices more functional and accessible, even in countries like India where affordability is a critical factor.
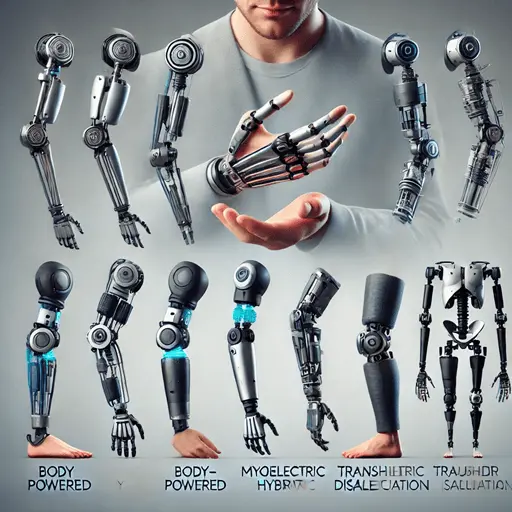
Types Of Prosthetic Hands

Choosing the right prosthetic hand depends on several factors including functionality, aesthetics, cost, and lifestyle needs. Here's a breakdown of the most common types of prosthetic hands:
A. Passive Prosthetic Hands
These are primarily cosmetic in nature. They look like real hands and can help restore body image, but they offer limited or no functionality. They are lightweight, easy to wear, and affordable.
B. Body-Powered Prosthetic Hands
These prosthetics use cables and harnesses to allow the user to control the hand’s movement using shoulder or upper arm movements. They are durable and less expensive than electronic hands, making them a common choice for users with limited budgets.
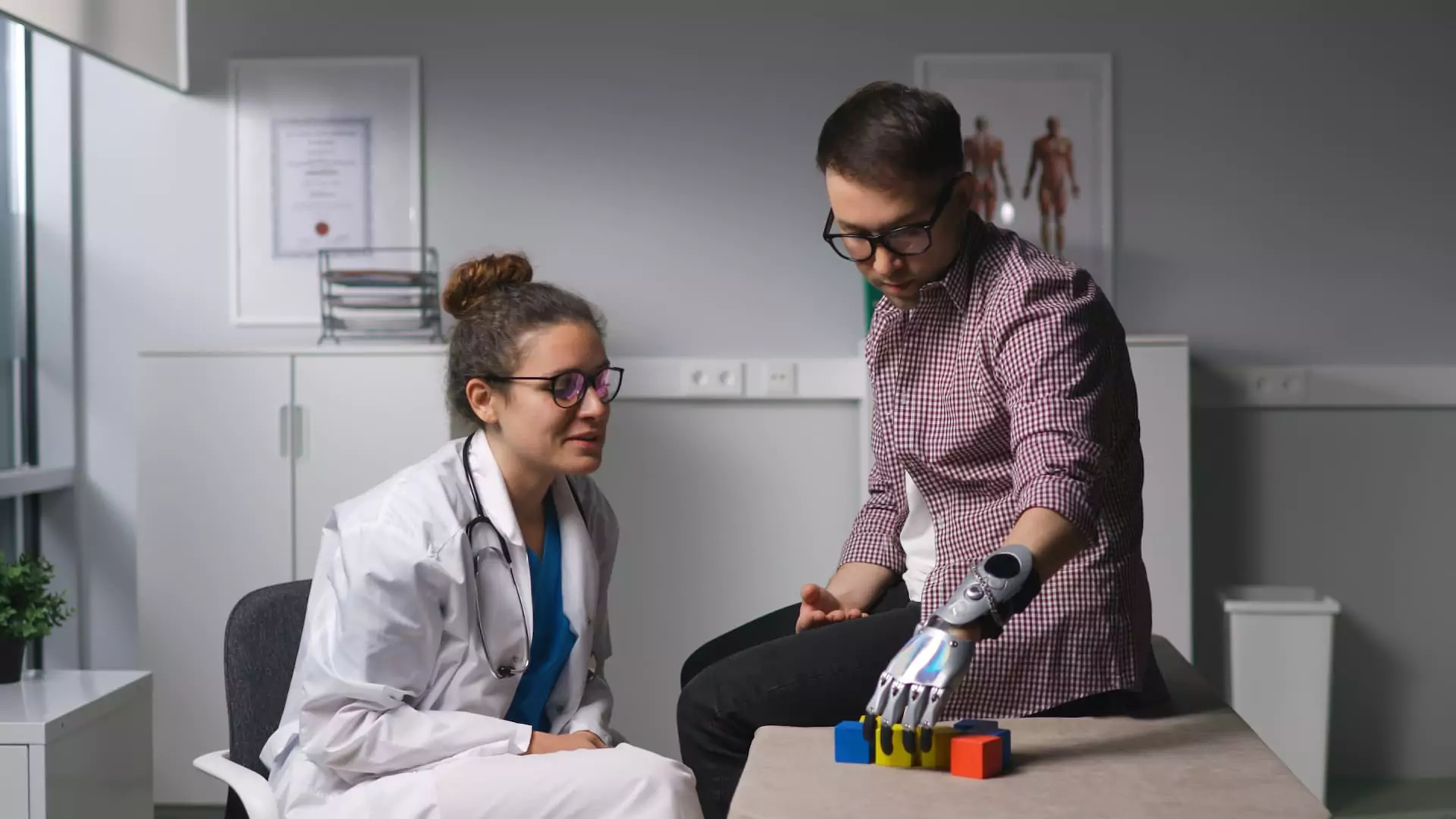
C. Myoelectric Prosthetic Hands
These are highly advanced prosthetic hands that use electrical signals from the user’s residual muscles to control movement. Sensors are placed on the skin, which detect muscle contractions and translate them into movements like opening or closing the hand.
D. Hybrid Prosthetic Hands
These combine features of both body-powered and myoelectric systems. They are suitable for people who need both power and precision but may come at a higher cost.
E. 3D-Printed Prosthetic Hands
With the rise of 3D printing, prosthetic hands can now be custom-built quickly and at a lower cost. These are often used for children who may outgrow their devices or in low-resource settings where affordability is key.
Each type offers distinct benefits and trade-offs, so working with a prosthetist to find the right match for your needs is essential.
How Do Prosthetic Hands Work?
Understanding how prosthetic hands work is crucial in selecting the right type and setting realistic expectations for their function.
A. Basic Functionality
- Passive hands may have adjustable fingers or a static grip to assist in activities like pushing or holding items.
- Mechanical hands are controlled manually through a body harness and cable system.
- When the user moves their shoulder or upper arm, the motion pulls the cable, opening or closing the hand.
B. Myoelectric Technology
- Myoelectric hands use electrodes that detect tiny electrical signals generated by muscle contractions in the residual limb.
- These signals are sent to a microprocessor inside the prosthetic hand, which activates small motors to move the fingers or thumb.
- Some advanced models can even differentiate between several types of grips—like pinching, grasping, or pointing.
C. Power And Sensors
- These prosthetics run on rechargeable batteries, usually lasting 12–24 hours on a full charge.
- Some devices incorporate pressure sensors or even haptic feedback to simulate touch or grip pressure.
D. Control And Training
- Users often undergo physical therapy and training to learn how to control the prosthetic effectively.
- Software may also be used for customizing grip patterns and responsiveness to match the user’s lifestyle.
In summary, prosthetic hands work by translating the user’s intent—through mechanical or electrical signals—into real-world hand movement, enabling a return to daily function.
Factors Affecting Prosthetic Hand Cost
| Factor | Description | Effect on Cost |
|---|---|---|
| Type of Prosthetic Hand | Passive/cosmetic (no mechanical/electronic parts), Body-powered (functional cables and mechanisms), Myoelectric (electronic systems, sensors, microprocessors) | Passive: Low Body-powered: Medium Myoelectric: High |
| Level of Customization | Custom sockets, tailored grips, silicone covers for aesthetic realism | Higher customization increases cost |
| Materials Used | Carbon fiber, medical-grade silicone, stainless steel; affects weight, comfort, durability | Premium materials = higher cost |
| Technology and Features | Multi-articulating fingers, programmable grips, Bluetooth connectivity, adaptive grasp, touch feedback | Advanced tech features significantly increase cost |
| Rehabilitation and Training | Post-fitting physiotherapy, training for optimal use | Adds moderate cost depending on duration and complexity |
| Maintenance and Repairs | Battery replacements, software updates, maintenance contracts | Ongoing costs, especially for myoelectric models |
The cost of prosthetic hands can vary significantly depending on several key factors. Whether you're seeking a basic functional design or a high-tech myoelectric hand, it’s important to understand what contributes to the overall pricing.
A. Type Of Prosthetic Hand
- Passive or cosmetic prosthetics are the most affordable, primarily because they don’t have any mechanical or electronic components.
- Body-powered prosthetics cost more due to the inclusion of functional elements like cables and control mechanisms.
- Myoelectric prosthetics, being the most advanced, are the most expensive due to complex electronic systems, sensors, batteries, and microprocessors.
B. Level Of Customization
- Prosthetic hands must be customized to fit the individual user’s residual limb.
- Custom sockets, tailored grips, and silicone covers for aesthetic realism can increase the cost.
C. Materials Used
- Materials like lightweight carbon fiber, medical-grade silicone, and stainless steel influence both weight and price.
- Higher-grade materials offer better comfort and durability but come at a premium.
D. Technology And Features
- Prosthetic hands with multi-articulating fingers, Bluetooth connectivity, and programmable grip patterns are significantly more expensive.
- Some even offer touch-sensitive feedback or adaptive grasp.
E. Rehabilitation And Training
Post-fitting care, physiotherapy, and training also add to the overall cost. These services help users maximize the functionality of their prosthetic hand.
F. Maintenance And Repairs
- Maintenance contracts, battery replacements, and occasional software updates (for advanced models) should also be considered when estimating total cost.
- Understanding these factors helps users and caregivers make informed choices based on functionality and budget.
If you’re exploring options for cosmetic or partial hand restorations, you might also like our detailed guide on Custom Artificial Finger Prosthetics. It explains how advanced silicone technology and precise customization can help restore both appearance and confidence for those with partial finger loss.
Prosthetic Hand Cost In India
| Category | Description | Estimated Cost (INR) |
|---|---|---|
| Cosmetic / Passive Prosthetic Hands | Primarily aesthetic; used for visual balance rather than function. | ₹10,000 – ₹40,000 |
| Body-Powered Prosthetic Hands | Controlled by cables and body movements; functional and durable. | ₹50,000 – ₹1,50,000 |
| Myoelectric Prosthetic Hands | Uses electrical signals from muscles for advanced control. | ₹2,50,000 – ₹12,00,000+ |
India is emerging as a hub for affordable and quality prosthetic solutions. The prosthetic hand cost in India ranges widely depending on the type, technology, and manufacturer.
A. Price Ranges (Estimated)
Cosmetic/Passive Prosthetic Hands: ₹10,000 – ₹40,000
These are primarily aesthetic and used for visual balance.
Body-Powered Prosthetic Hands: ₹50,000 – ₹1.5 lakh
Functional and durable, suitable for basic daily tasks.
Myoelectric Prosthetic Hands: ₹2.5 lakh – ₹12 lakh+
These offer advanced movement control and a high degree of functionality.
B. Why Are Costs Lower In India?
- Lower manufacturing and labor costs reduce the price significantly compared to Western countries.
- Local brands and clinics often collaborate with NGOs and government initiatives to make prosthetics more affordable.
C. NGO And Government Support
- Organizations like Jaipur Foot, BMVSS, and Otto Bock India provide low-cost or free prosthetics.
- Ayushman Bharat and other health schemes may offer partial reimbursement or support.
D. Imported Vs Local Prosthetics
- International brands such as Ottobock, Touch Bionics, and BeBionic are available in India but come at a premium.
- Locally made hands (including 3D-printed ones) offer functionality at a fraction of the cost.
- When planning for a prosthetic, it's crucial to include costs for fitting, follow-ups, and training, which can vary between hospitals and clinics.
Interested in cutting-edge prosthetic hand technology? Explore our detailed guide on Robotic Hand for Humans – Benefits, Best Options & Price of Bionic Hands in India for insights into how AI, multi-grip functions, and cost factors shape the future of upper-limb prosthetics.
Choosing The Right Prosthetic Hand
Selecting the appropriate prosthetic hand is not a one-size-fits-all decision. It should be based on individual needs, lifestyle, budget, and physical capabilities.
A. Assess Functional Needs
- Does the user need it primarily for aesthetic balance, or do they need to perform daily tasks like eating, typing, or dressing?
- Higher levels of activity may require a more functional, durable hand.
B. Consult A Prosthetist
- A qualified prosthetist can evaluate the residual limb, suggest suitable options, and ensure the best fit.
- They may also provide trial fittings or demos to help with the decision-making process.
C. Lifestyle And Occupation
- Someone with a sedentary job may benefit from a simple mechanical hand.
- A student or tech worker might benefit from a myoelectric hand with fine motor control.
D. User Age And Adaptability
- For children, cost-effective or adjustable 3D-printed hands may be ideal, especially since they'll outgrow prosthetics.
- Adults might invest in longer-term, durable solutions.
E. Budget Planning
- Plan not just for the prosthetic hand, but for ongoing maintenance, therapy, and upgrades.
- Making an informed choice ensures long-term satisfaction and effective use.
Accessibility And Availability In India
India has seen considerable growth in prosthetic availability, but access still varies by location and financial resources.
A. Where To Get Prosthetic Hands In India
- Hospitals and rehabilitation centers like AIIMS, NIMS, and private multispecialty hospitals offer prosthetic services.
- Prosthetic and orthotic clinics across major cities provide a range of solutions.
- Mobile prosthetic units are now reaching underserved rural populations.
B. Urban Vs Rural Accessibility
- In cities like Delhi, Mumbai, and Bengaluru, access to advanced prosthetic hands is easier.
- In rural areas, NGO partnerships and mobile camps play a critical role in extending services.
C. Government And NGO Assistance
- Several NGOs provide prosthetics free of cost or at subsidized rates.
- Government welfare programs are also increasing the distribution of assistive devices in remote areas.
D. Awareness Campaigns
- Awareness drives and support groups are helping more people learn about their options and get fitted earlier in life.
- Despite infrastructure challenges, the availability of prosthetic hands in India is improving steadily due to innovations and collaborative efforts.
Care, Maintenance, And Lifespan Of Prosthetic Hands
To ensure a long-lasting and functional prosthetic hand, proper care and maintenance are essential. Each type of prosthetic requires different upkeep, but the overall goals are cleanliness, mechanical integrity, and responsiveness.
A. Daily Cleaning
- Wipe the prosthetic with a soft, damp cloth after daily use to remove sweat and dust.
- Avoid harsh chemicals that may damage the cosmetic covering or internal components.
B. Battery Charging (Myoelectric Hands)
- Charge the battery every night to ensure consistent performance.
- Use only manufacturer-approved chargers to avoid damage.
C. Periodic Adjustments
- Visit the prosthetist regularly for alignment checks or socket adjustments.
- Small changes in the user’s limb or posture can affect fit and comfort.
D. Mechanical Wear And Tear
- Cables, joints, and sensors may wear out over time, especially in body-powered or myoelectric hands.
- Most prosthetic hands come with a warranty of 1–3 years, after which repairs or replacements may be needed.
E. Typical Lifespan
- Passive prosthetics may last 5–7 years with minimal maintenance.
- Body-powered devices can last 3–5 years, depending on usage.
- Myoelectric prosthetic hands may last 3–4 years before requiring major servicing or replacement.
- Proper care not only prolongs the lifespan but also improves user safety and comfo
Success Stories: Real-Life Impact Of Prosthetic Hands
The true impact of prosthetic hands can be seen in the lives of people who’ve regained functionality, independence, and self-esteem.
a. Amit, 28, from Delhi
After a workplace accident led to the loss of his right hand, Amit received a myoelectric prosthetic from a private clinic. With training, he’s now back to his IT job, confidently typing and using a mouse daily.
b. Rekha, 15, from Rajasthan
Born with a limb difference, Rekha was fitted with a 3D-printed prosthetic hand through an NGO partnership. Lightweight and colorful, her prosthetic allows her to write, draw, and play with her peers.
c. Mahesh, 42, from Bengaluru
A construction worker who lost his hand in a machinery accident, Mahesh received a body-powered prosthetic through a government aid scheme. He can now handle tools and continue supporting his family.
These stories highlight that prosthetic hands don’t just replace a limb—they restore livelihoods, confidence, and joy.
Future Of Prosthetic Hands In India And Globally
Prosthetic technology is advancing at an unprecedented pace, and the future holds exciting possibilities for enhanced functionality, affordability, and accessibility.
A. AI-Powered Prosthetics
Integration of AI and machine learning is helping prosthetic hands learn user patterns and predict movements for smoother, more intuitive control.
B. Neuro-Controlled Hands
Experimental systems are using brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) to allow users to control prosthetic limbs with their thoughts.
C. Sensory Feedback
Future prosthetics may include advanced sensors that provide real-time touch feedback, simulating pressure, temperature, or texture.
D. Affordability Through Innovation
Open-source designs and 3D printing are making quality prosthetics more accessible in lower-income countries, including India.
E. Local Manufacturing Hubs
Indian startups and health-tech companies are now producing indigenous, low-cost prosthetics tailored to regional needs.
The future is promising—bringing more responsive, lifelike, and affordable solutions to millions of people globally. Want to know more or explore advanced prosthetic solutions tailored to you? Contact Mobility Solutions today to speak with our experts and find the best prosthetic technology for your needs.
Conclusion
Prosthetic hands represent a remarkable fusion of technology, medicine, and human resilience. Whether someone needs a simple cosmetic hand or an advanced myoelectric model, today’s solutions are more accessible than ever—especially in India.The journey doesn't end with fitting a prosthetic—it continues through rehabilitation, training, and adaptation. But with the right support, users can regain independence, function, and confidence in daily life.If you or a loved one are considering a prosthetic hand, consult with a certified prosthetist, explore NGO support options, and take the first step toward a more empowered future.
Explore prosthetic hands: types, how they work, cost in India, care, and 2025 tech updates — a complete guide for patients, users, and caregivers.










